Article ID
Last Reviewed Date
Product Version
Operating System
Description
This Know-How article outlines the steps to perform a Data Integrity Check for backup data stored in the backup destination (e.g. local destination, AhsayCBS, or other cloud storage).
The functions of the Data Integrity Check (DIC) is to:
- Identify and remove the files and/or folders in the backup destination(s) which do not appear in the index.
- Identify and remove the files and/or folders which appear in the index but do not actually exist in the backup destination(s).
- Identify and remove corrupted files from the backup destination(s) when the Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) During Data Integrity Check setting is enabled.
- Identify and remove partially uploaded (orphan) files from the backup destination(s) to free up storage space.
- Update the storage statistics for the backup set(s).
Solution
To perform a data integrity check, login to the AhsayACB / AhsayOBM user interface.
-
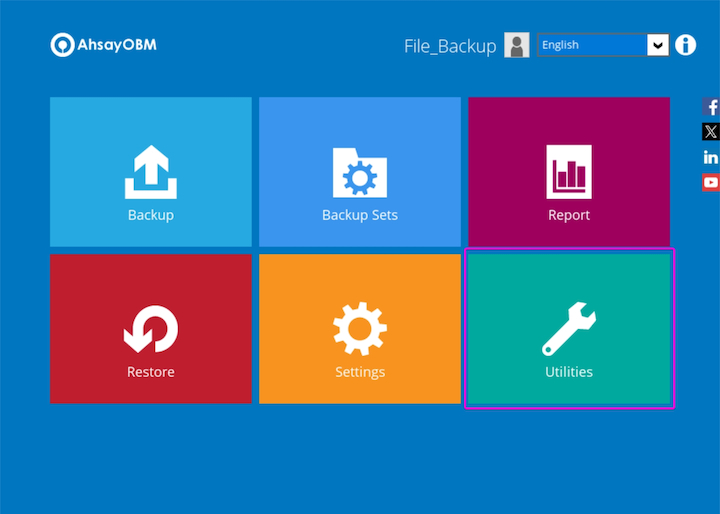
Login to the AhsayOBM / ACB user interface and select the Utilities tile.
-
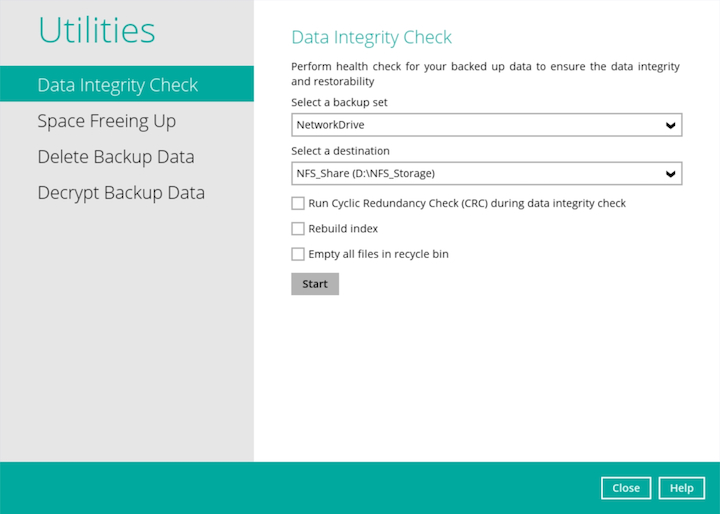
Select the corresponding backup set from the dropdown menu and then select the backup destination from the dropdown menu
-
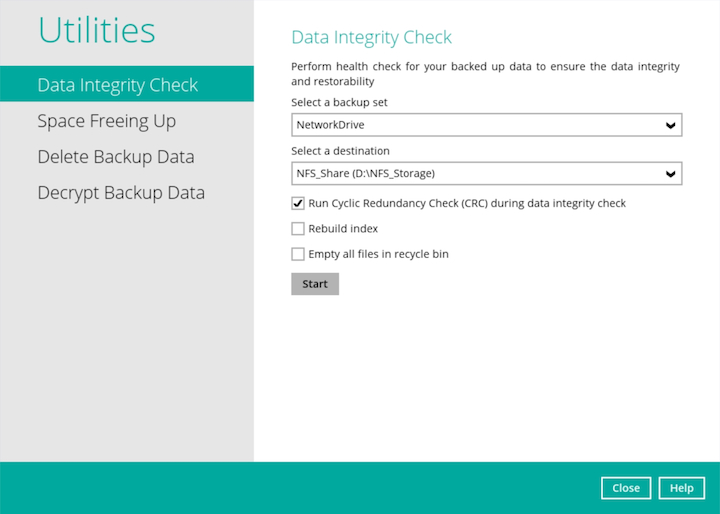
Enable the Run Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) during data integrity check option to check on integrity of the files against the checksum file generated at the time of the backup job.
-
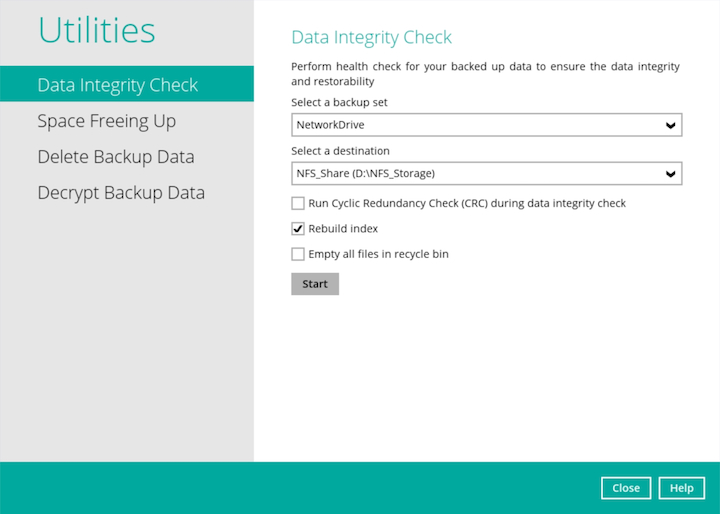
Enable the Rebuild index option to rebuild possible malfunction index in the backup destination.
-
Enable the Empty all files in recycle bin option to permanently delete the data blocks in the Recycle Bin.
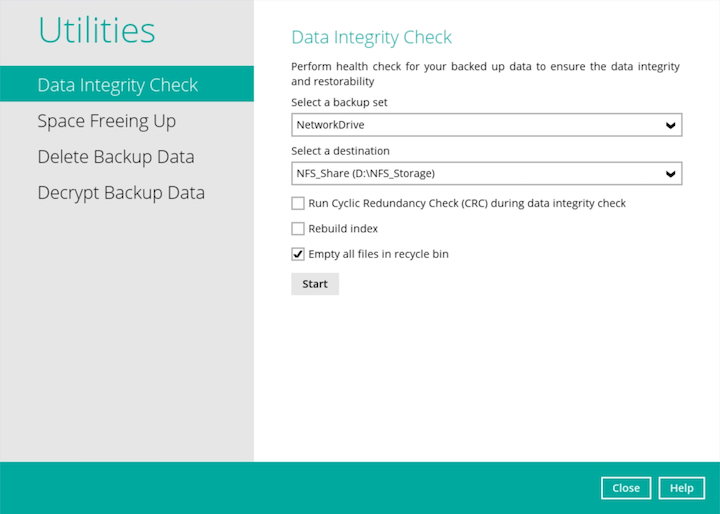
- Then press the Start button to start the data integrity check.
-
A data integrity check can only be performed when there is no manual / scheduled backup job in progress (of the corresponding backup set). It is highly recommended to temporarily disable the backup schedule to ensure that no scheduled backup is started while the data integrity check is still running.
The following error message will be displayed to indicate that the data integrity check had skipped a backup set with active backup job
Skipped Backup Set="Backup Set". Reason = "Backup Job "Backup Set" is still running."
Finished data integrity check with error on backup set "Backup Set (Backup Set ID) - The time required to complete a Data Integrity Check depends on a number of factors, such as the number of files/folders in the backup set(s), the bandwidth available on the client computer, hardware specifications of the client computer such as the disk I/O and CPU performance, and if there are other resource-intensive job running.
- If the CRC (Cycle Redundancy Check) option is enabled, backup data will be streamed from the backup destination (e.g. the cloud storage location or FTP location for example), to the client computer in order to perform the CRC check. This may incur additional charges from your Cloud Storage provider. For users with a metered internet connection, this could result in additional charges by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).
- During a data integrity check, pay attention to the resource usage on the client computer.
- Consule with your cloud service provider to ensure that CRC checks are performed regularly for your data.
- For backup destinations on cloud storage services, such as Amazon S3, data integrity checks are expected to be performed by the cloud storage service provider.
According to Amazon S3 FAQs (https://aws.amazon.com/s3/faqs):